Company Overview
Enterprise Risk Management : ERM
Risk management:Board of Directors assign Risk Management Committee to administrate the risk management policy and for the agency to use as guidelines and strategies to manage risks and continuously report to the company’s executives. The company has adopted the “Three Lines of Defense” risk management framework, which is divided into three groups
First line of defense means a business unit that carries a risk, responsible for identifying and managing risk directly (Design and Implementation of Controls) These business units must prioritize risk management as key elements in their operations.
Second line of defense means Regulatory Compliance Unit, responsible for ongoing monitoring of the design and implementation of controls in the first level responsible. Include suggestions and facilitate risk management activities. Most of them are management functions that may have some degree of neutrality. But not completely independent of the first level responsible.
Third line of defense means Internal Audit Responsibilities are independent of the risk management.



The company’s key risk management process is to: 1) Identify risk factors that may affect the company’s operation significantly. 2) Risk assessment and risk monitoring process to be in an acceptable level. And 3) Reporting on various types of risks and issues as follows:
- 1.Strategic Risk
Means the risks arising from the establishment of a strategic plan; inappropriate or unsuitable for internal factors and external environment as a result, the vision and mission are not fulfilled. - Operational Risk
Means a risk that will cause damage. It may be caused by failure,inadequacy or inappropriateness of internal processes, personnel, systems,or external factors that may affect the operation and / or financial status,reputation and credibility of the company or lack of supervision and good governance or lack of corporate governance within the organization- The Company has set policies, plans and operational risk management framework in line with the company’s policy. The policy is communicated to all agencies to practice strictly also considered the scope of risk management to cover the following six core activities:
- Insurance Consideration
- Product Design and Development
- Determining the premium rate
- Claim Management
- Reinsurance
- Investment in other businesses
- The Company has set policies, plans and operational risk management framework in line with the company’s policy. The policy is communicated to all agencies to practice strictly also considered the scope of risk management to cover the following six core activities:
- Insurance Risk
Refers to the risk caused by fluctuations in frequency, intensity and the time of the damage deviates from assumptions used to determine the premium rate, calculation of insurance reserves and consideration of the insurance. Insurance risk factors, such as premium rates, concentration of the disaster or the cost is higher than the assumed cost, allocation of premium reserve, insurance claims, change of behaviour of policyholders, insureds, and the development of new insurance products, which may affect the number of claims and expected future cash flow - Marketing/Investment Risk
Means the risk that changes in the market price of an investment asset, interest rate, exchange rate, foreign currency, derivative and commodity prices. - Credit Risk
Means the risk that a partner / contract is causing, inability to repay the debt or failure to comply with the contract with the company or the opportunity of the counterparty / partner is downgraded the credit rating. - Liquidity Risk
Means the risk caused by the fact that the company is unable to pay off liabilities or obligations by due date because the company cannot change the assets into cash or not be able to adequately finance the capital to accommodate the potential risks in the business. - Risk of compliance with rules, regulations and other laws related to business operation
Means the risks arising from failure to comply with the rules and regulations relating to the business operation of the agency responsible for regulating and supervising the business and other laws associated. - Risk of Disaster
Means the sudden and serious damage that may cause enormous losses, such as damage from earthquakes, floods, as there are currently large natural disasters occur. This is an important factor that may affect the business operation of the company. However, approvals of insurance of the company are only for health and accident but if there is a disaster, it can cause a major compensation.

Monitoring,Evaluating and Reporting
Monitoring and evaluating are the process that will continue from whereas the company defines risk management plan and the person responsible for managing the risk. The goal is detailed as follows:
• To assess the suitability and effectiveness of risk management methods including follow-up management and the risk achieved whether the objectives of the risk management have been fulfilled.
• To control and monitor the level of risk.
- To determine whether control measures have been redefined or adjusted to reduce the likelihood or effects of risk effectively.
- To determine who is responsible for the evaluation and bring the evaluation results to report to the Risk Management Committee
Benefits of Risk Management
To prevent and reduce losses from disaster which may disrupt or discontinue the business operation.
The company will consider carefully whether the level of risk transferred is at the acceptable level and does not refer the handbook of premium rate set up. To monitor and control the distribution of risks must be appropriate, not concentrated by geography or type of risk. The risk higher than the company can be obtained alone is managed to transfer the risk to the insurer through the insurance contract. The selection of the reinsurer is considered on financial stability as the first priority in order to manage the insurance to the appropriate proportion of insurance in terms of the sum of the results of the insurance and to be consistent with the objectives and goals of the company.
Risk Management for Claims Management and Reserves
To determine the amount of insurance reserves, the company uses the generally accepted actuarial method to calculate and certify by authorized actuaries. The changes in reserves are monitored and analysed to determine factors that may affect the company’s reserves regularly to ensure that sufficient reserves for the obligation the company is bound to the insured in the future. The actuarial shall assess the appropriateness and adequacy of the reserves.
Risk Administration/Management of Reinsurance
The risk higher than the company can bear alone will be transferred to the reinsurer through the insurance contracts both advance–annual type and individual type. The selection of the reinsurer is considered on stability first. In addition, the company has insurance portfolio management to appropriate the proportion of insurances in terms of the total of insurance approval results to be consistent with the objectives and goals of the company.
In addition, the company has developed a written reinsurance management strategy to comply with the rules and the requirements of the Office of Insurance Commission which is part of the management framework, overall risk and been approved by the Risk Management Committee and the Board of Directors, respectively consisting of the process of choosing the right reinsurance plan and implementation used for monitoring, review, control and documentation of the company’s reinsurance considering the acceptable risk of the company, financial costs by comparing the liquidity,trend of reinsurance market so that the company’s business plan is appropriate to the nature, size and complexity of the company’s business.
Asset and Liability Management (ALM) is the management of assets and liabilities in the financial statements. It also includes commitments to get returns and risks at an acceptable level. Risks involved are the risks that arise from liquidity management, interest rates and the risk of error pricing. Risks from inaccurate estimation of claim liabilities for example, when the company has to repay its debts and obligations but is unable to change assets available to be cash in time or cannot find sources of finance or can find sources of finance, but the financial cost is too high which will affect revenue and the capital and the reliability of the company.
The asset and liability management strategy emphasize the maintenance of financial liquidity to adequately cover liabilities to policyholders and number of policies. Liabilities as per policies is essential for the company to make investment decisions in terms of time to invest and interest rate risk.

Note
• Account price refers to assets and liabilities measured in accordance with financial reporting standards.
- Appraisal price ราคาประเมิน refers to the assets and liabilities assessed as per the Notification of the OIC regarding valuation of assets and liabilities of non-life insurance companies for the primary purpose of directing financial security of insurance companies and to ensure that the company has the ability to fully pay benefits to the Insured.

Value, methods and assumptions in assessing liabilities from insurance contracts
Liabilities from insurance contracts consist of:
1. Unearned Premium reserve
The company calculates premium reserve not counted as income in accordance with the Notification of the OIC Re: Rules, Procedures and Conditions for allocation of premium reserve not counted as income, reserves for claims and other reserves of non-life insurance companies by calculating the method 1/365 System
- Claim reserve and outstanding
Claim reserve and outstanding are recorded when claims are logded by the insured at the value appraised by the independent appraiser or the company’s appraiser depending on the case. In addition, the company has made additional provision for claims that have not yet been reported to the company (IBNR), as assessed by the actuarial. - Unexpired Risk Reserve
An unexpired risk reserve is the best estimate of the insurance claims that are expected to occur during the remaining insurance period for an insurance policy that is still in force according to an analysis of past claims by an actuary. Unexpired Risk Reserve will recognized in the financial statement when the unexpired Risk Reserve over unearned premium reserve.
3 methods of mathematical analysis are used in assessment.
- Chain Ladder method (CL) for claims data and claims occurred
- Bornhuetter-Ferguson method (BF) for claims data and claims occurre
- Expected Loss Ratio (ELR) To estimate the best value of claims, we mainly use CL to accommodate claims for damages while BF and ELR methods used on appropriateness of data.

Note
- Book Value refers to the value of the insurance contract assessed in accordance with accounting standards. The main objective is for investors to financially analyze to understand the economic value of a recognized insurance liability accepted in accordance with accounting principles in Thailand. Such value must be certified by a licensed auditor.
- Appraisal value refers to the value of liabilities from the insurance contract as assessed by the Notification of the OIC re: appraisal of asset value and liabilities of insurance companies for the primary purpose of overseeing the financial security of
insurance companies to ensure that the company has the ability to fully pay the insured, which must be assessed by licensed actuaries approved by the actuarial registrar. The assumptions used in the appraisal must be consistent with the actual experience or, if the company has insufficient information, may be based on industry experience and tailored to the specific characteristics of its insurance portfolio. This includes the Provision of Adverse Deviation (PAD), which is in line with the regulation of the OIC.
Observation remark
In some periods of financial reporting, the amount of insurance liability may differ between the accounting value and the appraised value significantly due to the different objectives and methods of assessment as described above. The person who will use the
information should study and understand the purpose of the valuation method of the insurance contract both thoroughly before making a decision.
Investment Policy is to be in line with the overall risk management policy, product design, insurance issuance, insurance contract, asset and liability management, capital status, acceptable risk level, expected return and the availability of systems and personnel to support investment and comply with the Notification of the OIC re: other businesses of insurance companies 2013
Objective
The purpose of this policy is to assist Pacific Cross Health Insurance PCL in order to manage its assets efficiently. To oversee, monitor and evaluate its assets of the company and investments in those assets will be held by the Investment Committee by taking into account of the business liquidity for the benefit of the company’s mission and objectives. This policy is consistent with the laws and regulations of the OIC.
(คปภ.)
Proportion of investment by asset type (Product Limit)
The company has an investment policy in the year 2017 with the objective “to emphasize security of principal and value of return on investment”, which determines the proportion of each type of investment to suit the condition of capital market at that time. Considering the consistency of each type of investment with risk management, which must be approved by the Investment Committee, then presented to the Managing Director for an approval before proceeding every time.
Strategy and allocation must be based on the current situation of the company to consider the liquidity as the first priority. This includes investment limits. Investors must keep track of economic movements and regularly analyze data from financial institutions and research centres of many reliable companies. In addition to investment planning, the flexibility of the investment plan is enhanced if the money market or capital market is fluctuated.

Asset quality
- Cash and Cash Equivalent– is a deposit with domestic and foreign financial institutions established under the laws of each country. Depositing funds with foreign financial institutions is for specific purposes for use in their respective country.
- Fixed Deposit / Term Deposit – Organizations can deposit money with either government or private banks where there is the guaranteed principal. The interest rate will be compared to the current market rate as well as the exchange rate. The duration of the fixed deposit should start from 3 months to 60 months as the maximum.
- Debt instrument – Quality of debt instrument i.e. bonds or debentures are selected based on credit rating, which must be at least “A-1”, rated by reputable and reliable companies both domestically and internationally. The company is considered to have the ability to conduct business well.and the time frame bonds and debentures should be in 3-5 years.
- Mutual Funds – Mutual funds must have a policy to invest in or hold high quality debt securities or equity instruments so that the return is appropriate to risks, such as treasury bills, government bonds, Bank of Thailand bonds, state enterprise bonds, debt securities issued by legal entities by specific law, debt securities issued by state-owned enterprises or commercial banks or foreign banks or debt securities by commercial banks or private companies with reliable credit rating investable.
Asset Valuation
The company has invested in assets in cash, deposits with financial institutions, depositories, and negotiable certificate of deposit
1. Cash – appraised by the amount available.
2. Deposits – with financial institutions and deposit slip appraised by the deposited amount and deposit slip appraised at cost
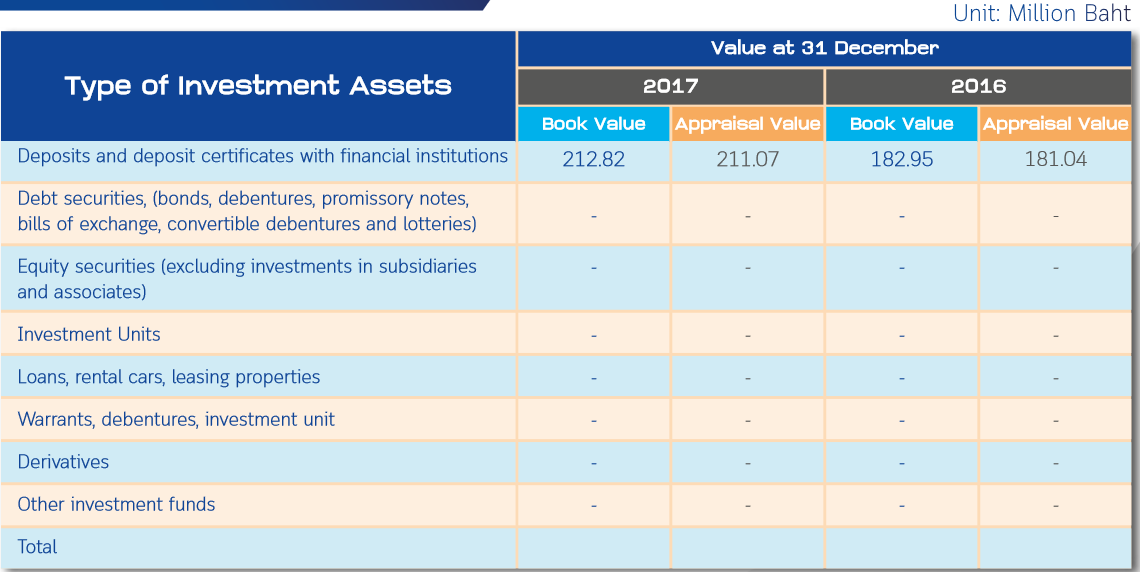
Note
Book value refers to assets and liabilities assessed by the Financial Reporting Standards.
Appraisal refers to assets and liabilities assessed according to the Notification of the OIC re: the valuation of assets and liabilities of insurance companies for the primary purpose of overseeing the financial security of insurance companies and to ensure that the company is able to fully cover the Insured ‘s insurance benefits.









